Personal beliefs, values, attitudes and behaviour
The diagram below illustrates the influences on us that result in our behaviour and whether that resulting behaviour is ethical. The diagram first outlines the sources of our beliefs. It then shows the relationship between the beliefs and values to our attitudes and our resulting behaviour.
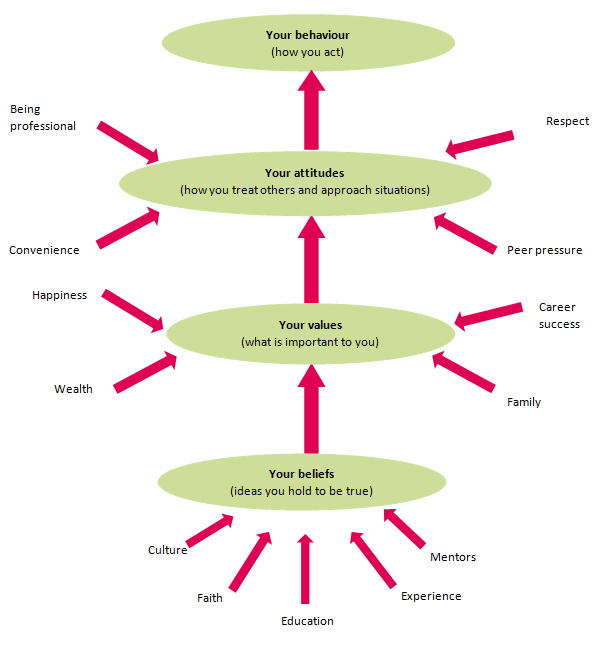
What is a belief?
A belief is an idea that a person holds as being true.
A person can base a belief upon certainties (e.g. mathematical principles), probabilities or matters of faith.
A belief can come from different sources, including:
- a person’s own experiences or experiments
- the acceptance of cultural and societal norms (e.g. religion)
- what other people say (e.g.education or mentoring).
A potential belief sits with the person until they accept it as truth, and adopt it as part of their individual belief system.
Each person evaluates and seeks sound reasons or evidence for these potential beliefs in their own way.
Once a person accepts a belief as a truth they are willing to defend, it can be said to form part of their belief system.
What is a personal value?
Values are stable long-lasting beliefs about what is important to a person. They become standards by which people order their lives and make their choices.
A belief will develop into a value when the person’s commitment to it grows and they see it as being important.
It is possible to categorise beliefs into different types of values – examples include values that relate to happiness, wealth, career success or family.
A person must be able to articulate their values in order to make clear, rational, responsible and consistent decisions.
What is an attitude?
Attitudes are the mental dispositions people have towards others and the current circumstances before making decisions that result in behaviour. People primarily form their attitudes from underlying values and beliefs.
However, factors which may not have been internalised as beliefs and values can still influence a person’s attitudes at the point of decision-making. Typical influences include the desire to please, political correctness, convenience, peer pressure, and psychological stressors.
Note
The potential for these influences to sway attitudes will be greater if the person has not clearly thought through their beliefs and values. This process includes considering the principles by which they might reconcile or prioritise competing values.
A lack of self-awareness or critical insight, or the presence of ambivalence or uncertainty about values, can lead to a less rational attitude to choices, and ultimately to undesirable behaviour.
